The Crucial Intersection of Cybersecurity and Cyber Insurance
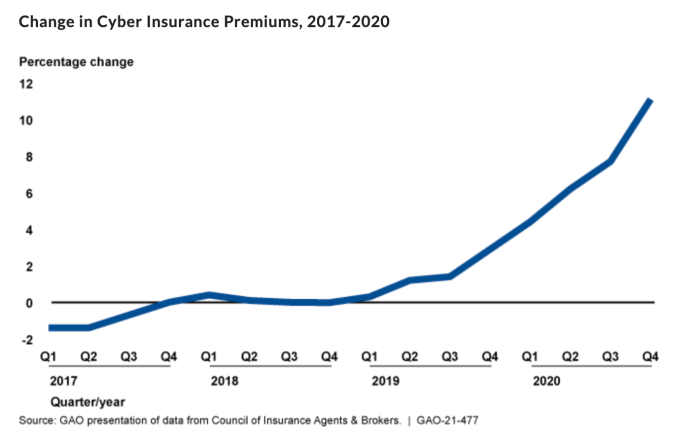
In today’s digital era, the intersection of cybersecurity and cyber insurance is becoming increasingly important. As threats evolve and become more sophisticated, businesses must enhance their security measures to mitigate risks and meet the qualifications for cyber insurance. But at the same time, qualifications for insurance underwriting are becoming more stringent and policy premiums are rapidly rising. According to data compiled by the Government Accountability Office (GOA), key trends in cyber insurance include lower coverage limits in high-risk sectors and rising premiums.
The Role of Multi-Factor Authentication in Cybersecurity
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) plays a critical role in bolstering security. By requiring users to provide multiple forms of identification, MFA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access to systems and data. This is crucial as it only takes one compromised user credential or service account to seriously damage and disable an organization.
The Zero Trust Model: A New Paradigm in Security
The Zero Trust model, which operates on the principle of “always verify,” is a new paradigm in cybersecurity. This model recognizes that inherited or implicit trust and a network-centric approach to security are suboptimal. Instead, it emphasizes that organizations should trust no one, whether inside or outside their networks, without verification.
Benefits of Multi-Factor Authentication in a Zero Trust Environment
Implementing MFA within a Zero Trust environment brings considerable benefits. It supports users to perform their jobs from anywhere using any device without introducing unnecessary risk. Furthermore, by improving identity security technology, organizations can better protect against cyberattacks, which is the first line of defense in a Zero Trust approach.
Meeting Cyber Insurance Qualifications with MFA
As cyber insurance providers increasingly recognize the value of robust cybersecurity measures, implementing MFA and Zero Trust may become prerequisites for coverage. This not only bolsters an organization’s security but can also help meet the qualifications for cyber insurance, offering protection against potential financial losses from cyber threats.
With cyber risks escalating and business interruption losses increasing, insurance carriers are becoming more stringent in their underwriting practices for cyber insurance policies. In response to these evolving threats, companies need to adopt more robust cybersecurity measures, including the implementation of Zero Trust frameworks and Multi-factor Authentication, to meet these heightened qualification standards.
The upward trend in cyber threats and the subsequent tightening of underwriting standards suggest that the costs and qualifications for cyber insurance could become more challenging in the future. The sooner businesses adopt robust cybersecurity measures and secure an insurance policy, the better positioned they will be to safeguard their operations and mitigate the financial risks associated with cyber threats.
As the cybersecurity landscape continues to evolve, so too will the intersection of cybersecurity and cyber insurance. By embracing approaches like MFA and Zero Trust, businesses can better protect themselves from threats and meet the demands of cyber insurance providers. In this ever-evolving digital world, it’s clear that robust cybersecurity measures are no longer optional – they’re a necessity.



