What to look for in cloud services providers
There is a battle going on in the cloud. If you follow the big players in the cloud space, you may be familiar with JEDI — which has nothing to do with Starwars. Instead, JEDI is the Pentagon’s Joint Enterprise Defense Infrastructure (JEDI) contract. JEDI is a 10-year contract that endeavors to modernize and unify the military’s IT operations and is valued at an initial $10 billion. Amazon’s AWS was the odds on favorite to win the contract but Microsoft’s Azure beat them out when the contract was awarded last October. A legal battle has ensued and a judge has ordered a stay on proceedings after Amazon filed a request for an injunction. Amazon’s AWS has been a clear leader in cloud market share but Microsoft’s Azure has been rapidly closing the gap. In the cloud space, the JEDI contract represents more than just $10bn in revenue — in some regards, it represents who is king of the hill. When choosing a cloud service provider, market share is one aspect we will look at but isn’t the only factor you should consider.
Cloud Service Providers By Market Share
As of 2019 fourth-quarter earnings, AWS revenues made up 11% of the $87.4bn in total quarterly sales holding their position as market share leader by cloud revenue. However, Microsoft’s Azure grew revenue by 62% in the fourth quarter compared to AWS’s revenue growth of only 34%. Microsoft doesn’t break out Azure revenue totals in their financials but based on data from Canalys, Azure’s market share comes in at 17.6% behind AWS’s 32.4%.
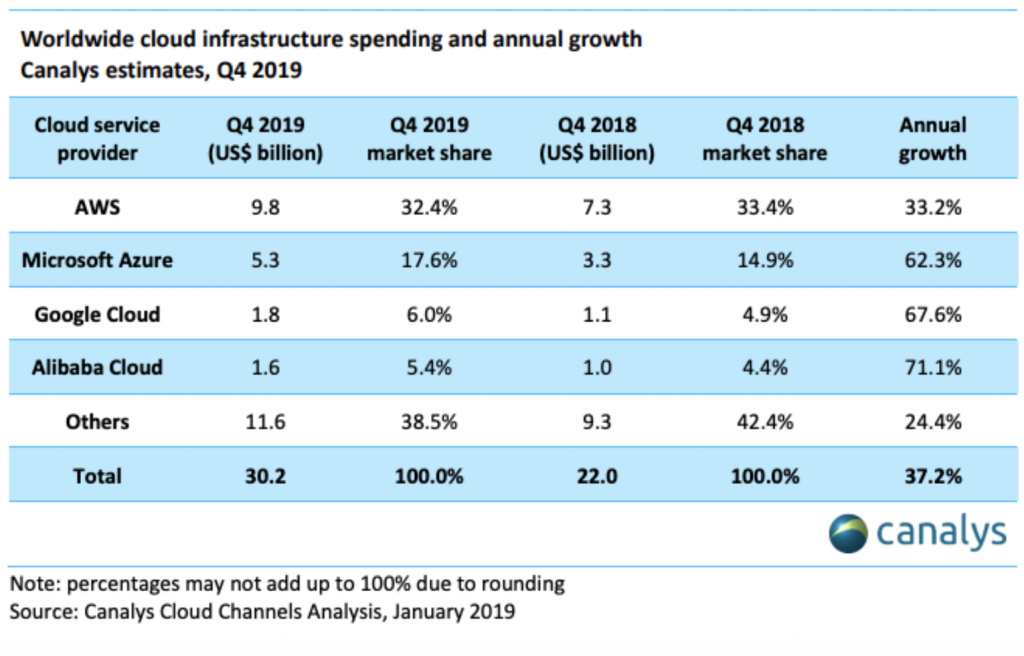
AWS has the advantage of a 7-year head start in the industry but the competition is gaining ground rapidly. Coming in third place was Google Cloud with revenue of $2.6bn and a growth rate of 53% from the previous year. Like Microsoft, Google is investing heavily in cloud growth as they each vie for a larger share of this new and rapidly growing industry.
Cloud Services
According to Synergy Research Group, cloud services grew at an increased rate of 24% in 2019 compared to 2018. This growth is largely centered around the three main cloud service segments of: Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS) or Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS).
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS is by far the most common of the cloud services. Through SaaS, a cloud provider allows end-users to login directly to software applications without the need to install and maintain the application on a local device. Users can manage, store and analyze their own data while the SaaS provider handles application updates and data center requirements.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Access to a cloud environment where you can manage, host and even develop applications. PaaS, cloud providers often make their own testing and development tools available within the platform.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
On-demand access to networking, storage and servers. Instead of co-locating or leasing your own hardware within a data center, IaaS allows for flexible hardware resources that can easily scale with your computing and storage needs within the provider’s infrastructure.
Private Cloud
Another consideration, based on your individual needs, is the opportunity for a private or even hybrid cloud solution instead of being solely reliant on one of the larger public clouds. Even AWS has had devastating outages and because it is the largest provider, it’s outages can take thousands of sites offline. In many cases, a private cloud can offer a lower total cost of ownership (TCO) while also providing more efficiency, control and customization. Many organizations look to a private cloud when security, data privacy and compliance are driving factors.
Finding the Right Cloud Services Provider
When looking for a cloud services provider, you will need to understand which cloud service segment will best fill your needs. You will then be able to weigh the various benefits within SaaS, IaaS and PaaS such as increased scalability, security and flexibility. Many organizations look to a Managed Services Provider (MSP) in making their decisions. MSPs have become a critical component in cloud management for most organizations



