Nearly 75 Percent of Malware Evades Signature-Based Protections
Earlier this month, WatchGuard Threat Labs released their Q1 2021 Internet Security Insights report. The report highlights data taken from multiple security services available on Firebox appliances. For those who live and breathe cybersecurity, the quarterly Threat Labs analysis of real-world attack data on real networks is greatly revealing. The report offers incredible insight into global attack trends and can help identify weaknesses in current security policies. WatchGuard users opt-in to sharing the data through Firebox security services including:
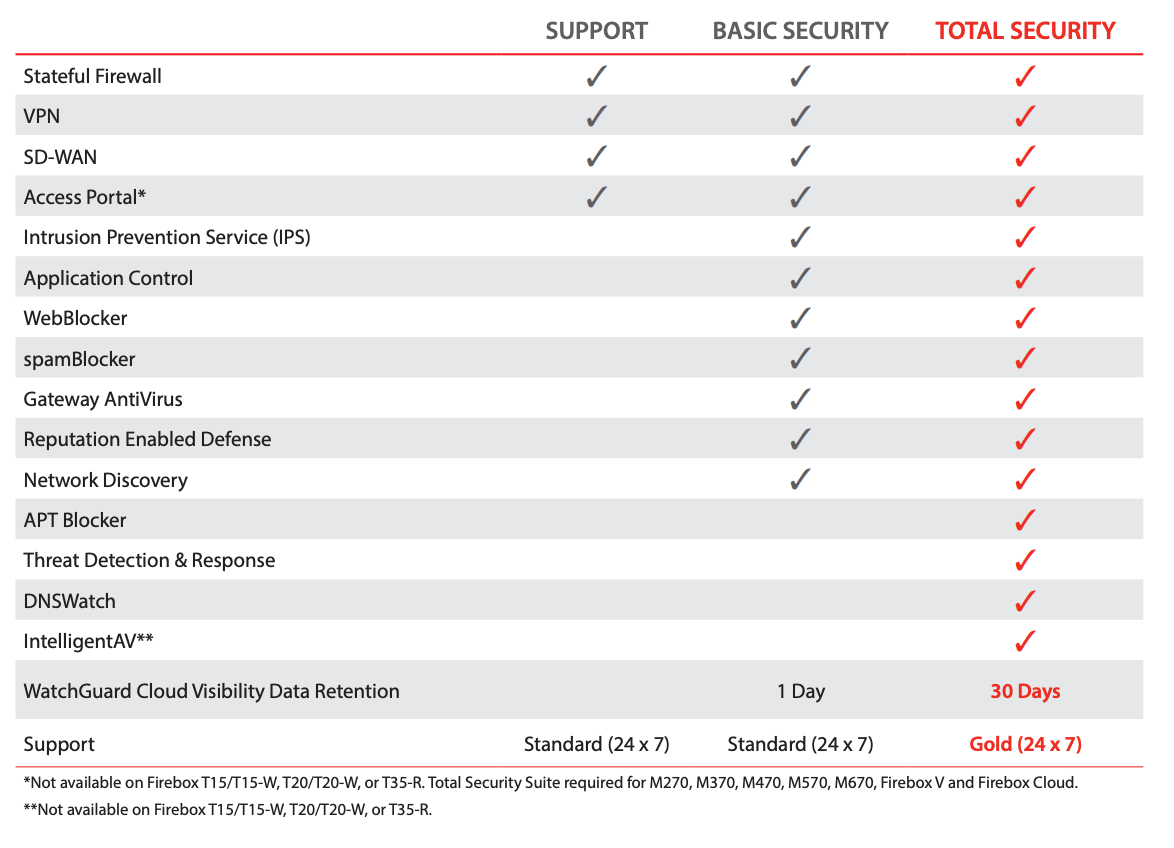
- Gateway AntiVirus (GAV): Signature-based malware detection
- IntelligentAV (IAV): Machine-learning engine for malware detection
- APT Blocker: Sandbox-based behavioral detection for malware
- Intrusion Prevention Service (IPS): Detects and blocks network-based, server and client software exploits
- DNSWatch: Blocks various known malicious sites by domain name
In the reporting quarter, Firebox appliances reported a significant increase in total attack volume. Attacks surpassed the 4 million mark for the first time since Q1 2018. And for the first time ever, evasive zero-day malware detections were more prevalent than traditional signature-based malware detections. Nearly 75% of all detections were classified as zero-day meaning there was no signature-based protection against the threat at the time of detection.

We identified more advanced zero-day malware this quarter by volume than any other quarter. By now, any security expert worth listening to will tell you that traditional signature-based protection just won’t cut it. During Q1, just under three-fourths of the total malware evaded signature-based detections. Without a signature to detect if the file contains malware, administrators must use other means to identify the threat. Use advanced anti-malware services that proactively catch new threats, such as behavioral sandboxes that can detect the true intentions of suspicious files. These services must also include anti-sandbox detection as modern malware can identify when they are being simulated and stop execution to evade detection.
Defending against zero-day attacks requires more than the traditional signature-based protection. Today threats evolve and are distributed far faster than signatures can be updated. An effective detection method to identify a zero-day threat on its first sighting is to sandbox suspicious files in a safe environment to monitor their behavior before letting them onto the network. Tools such as the Firebox APT blocker do exactly that.
Along with identifying, sandboxing, and analyzing suspicious files, defending against zero-day threats is aided by completely blocking suspicious and potentially dangerous domains at the DNS level. Filtering at the DNS level, such as provided by WatchGuard DNSWatch and DNSWatchGO, protects users from phishing attacks as well as zero-day malware. In Q1, DNSWatch accounted for over 5 million blocked connections through domain filtering. APT Blocker and DNSWatch are both included in the WatchGuard Total Security suite.
If your security program is still relying solely on signature-based defenses, you’re leaving yourself virtually unprotected from the majority of attacks. Contact us today to learn how a layered approach to security can protect your data and your users from known and unknown threats even in a work-from-anywhere environment.



